Part01: What is Git, Install, and Config
So, here is Git, but what actually IS git?
Git definition
Git is an amzing code-management system. It is much better than other managements systems because of:
1. It CAN be decentralized, with proper workflow system.
2. It records ALL history of whole repository, but size is almost as same as others who do not save histories. AND you can reset code to ANY other time in history.
3. EVERYONE has an backup of the main repository, making the code strong.
4. It has lightweight branches and tags.
Git concepts
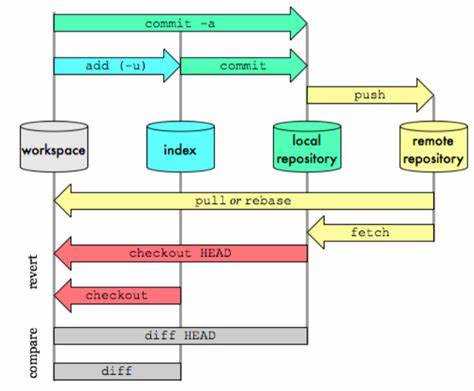
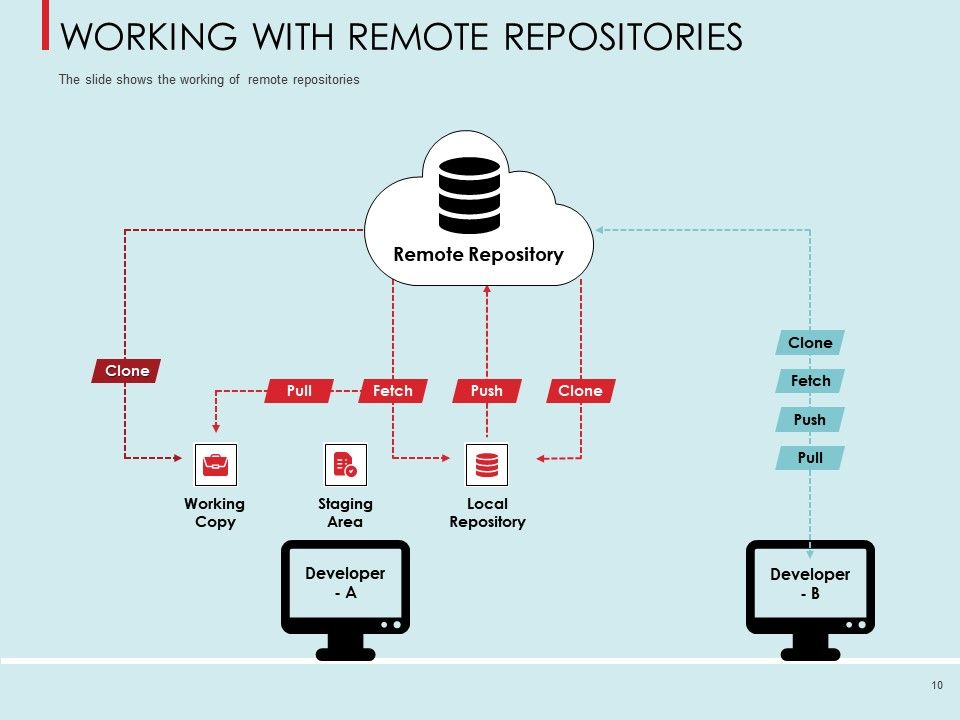
So here is the basic concepts of git. There are 4 places: The workplace, the index, local repository, and remote repository.
The workplace is what you see locally.
The index is a staging (cached) area for your works, you can stage things here to wait for commiting.
The repository is a database of your history and now commits.
The remote repository is a published version of the local repository.
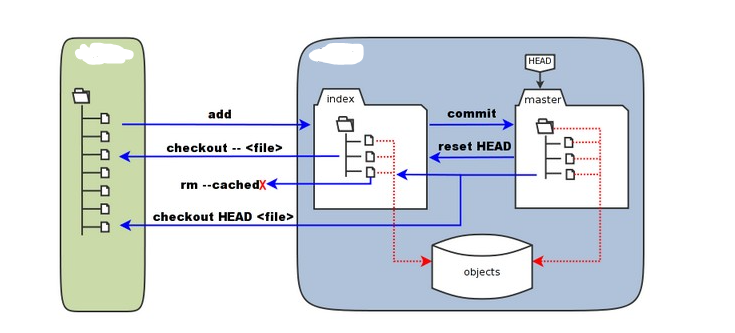
Explore: The local repository
There could many branches of a local repository, but how just changing the branch changes the whole working directory?
The answer is: HEAD. An repository stores snapshots of your codes, and name each branch with a HEAD.
When you are changing the branch, the HEAD changes, displaying a different snapshot, which changes the repository!